| Article found | Fact |
|---|
|
Secure Web services [Sh03]
|
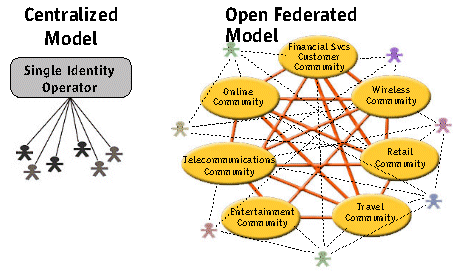
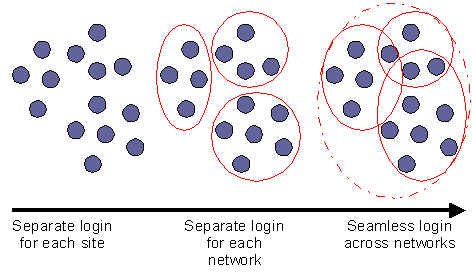
- todays WebSites and Enterprises have its own authentication method, and its own method of maintaining identity information and user profiles (identity crisis)
- today each site has inconsistent schemes for accessing and editing identity information
- each site has unclear and/or differing policy and privacy statements (few, if any, silo identity systems truly interoperate)
- Distinct identities and logins exist for building access, workstation login, application access, and remote access. Different applications require the user to reenter username and password, which don't interoperate. This makes managing Web properties, applications, identities, and policies nonscalable, and effectively prohibits the interaction (or even the association) of identities across applications or Web services.
|