 |  | | Contents: |  | |
 | | Related content: |  | |
 | | Subscriptions: |  | |
|
Download source code and use these tools with Globus
Vladimir Silva (vsilva@us.ibm.com)
OGSA developer, IBM
21 Oct 2003 Are
you struggling to manage user or host certificates on your development
grids? Here's some good news. Popular author Vladimir Silva has created
a set of Web and command line tools called Java Certificate Services,
and you can download his free source code. He created these tools to
help system administrators with the tedious task of managing user and
host certificates in development grids. Java Certificate Services is
written to work specifically with the Globus and the Java CoG toolkits.
Links to these tools are available in the Resources section of this
article.
Java Certificate Services overview
Java Certificate Services (JCS) provides the following functionality:
- CSR (certificate request) creation
- CSR signature
- X509 certificate creation (useful for GT3 user for host certificates)
- Self-signed (CA) certificate creation
JCS is built on top of the Java Crypto Extensions (JCE) used by Globus Toolkit version 3 to
implement the Grid Security Infrastructure (GSI). These JCE providers are
Cryptix and the Legion of the Bouncy Castle (see Resources).
Install JCS on a Windows or Linux host
Source bundles for JCS are provided in the Resources section of this article.
To install JCS, decompress the binary bundle into a folder on your host.
Note: You might need to build a binary distribution -- see the instructions below.
- On Windows systems, unzip the binary into a working folder such as
C:\
- On Linux systems, untar the binary bundle:
tar zxvf cert-services.tar.gz -–directory=/opt
Browse through the jCertServices-1.1 folder that's created and take a
look at the readme.txt or readme.html files for an in-depth description
of this software.
Deploy the Web-based tool on Tomcat
JCS provides a convenient Web-based tool that's easily deployed
on Apache Tomcat (see Resources) or any J2EE/servlet
container for that matter. JCS has been tested with Tomcat 4.1.27 and IBM WebSphere 4.x/5.x.
To deploy the Web-based tool and build the source, you will need Apache ant
(see Resources).
On Windows or Linux hosts, at the command prompt enter:
- In Linux:
cd /opt/jCertServices-1.1
- In Windows:
cd c:\jcertServices-1.1
-
ant -Dtomcat.dir="tomcat root" deployTomcat
Make sure to replace tomcat root with the full path to your Tomcat installation. For example: /opt/tomcat-4.1-27 (Linux)
Access the Web-based tool
To access the JCS Web-based tool, start your Tomcat server.
(This assumes the Tomcat server is installed and configured
on your system. See the server documentation on how to do this.)
Once the server is running, open a browser to the following URL:
http://localhost:8080/certservices/
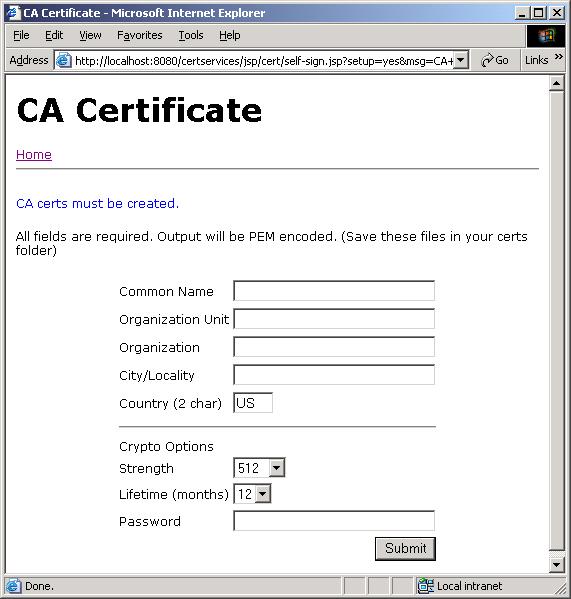
If everything goes well, you should see the CA certificate
installation dialog. A CA certificate must be configured first.
This certificate will be used later to sign any subsequent
CSR request or X.509 certificate.
Figure 1. CA Certificate installation page
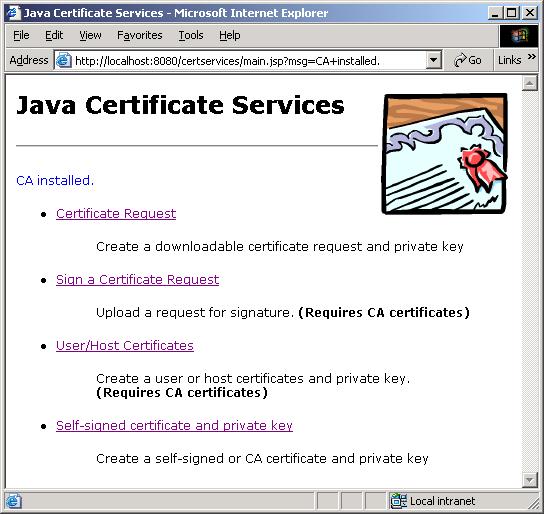
After the "root" CA certificate is installed, the main JCS menu is displayed.
Figure 2. The JCS Web tool main menu
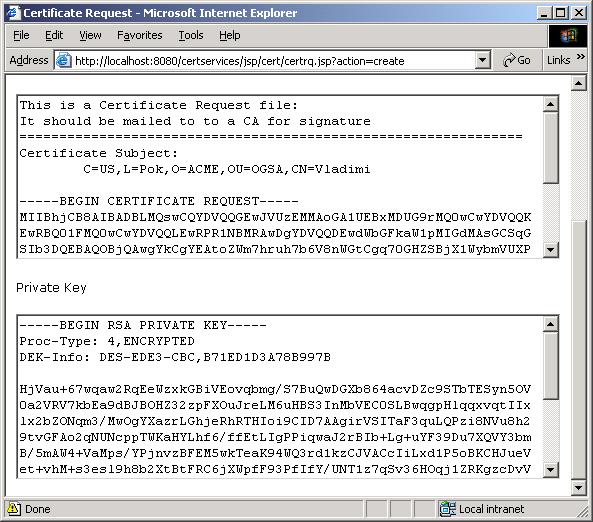
Create a certificate request
To create a certificate request, click on the JCS "Certificate Request"
main menu and complete the fields on the form. Save the output of your
certificate request and private key in two different files such as:
usercert_request.pem and userkey.pem.
Figure 3. Certificate request sample output
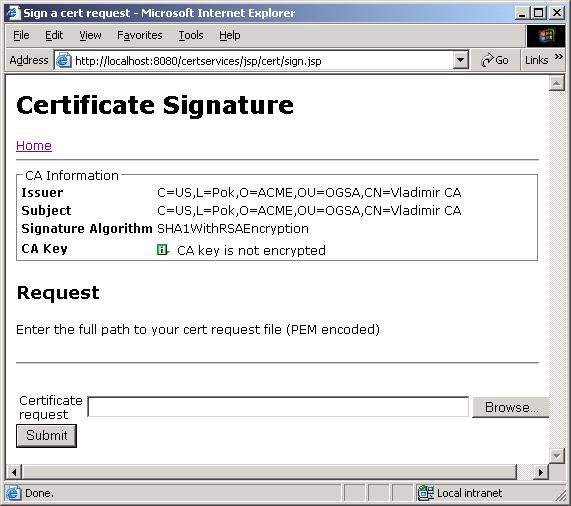
Signing a certificate request
To sign a certificate request, click Sign cert request from the main menu,
upload your CSR pem encoded file, and save the output to a file (usercert.pem).
Figure 4. Certificate request signature
Create a self-signed (CA) certificate and private key
Creating a self-signed (CA) certificate is easy with JCS.
Simply click the Self-signed certificate link from the main menu, fill
out the form values and save the certificate and private key contents
into two separate files: (cacert.pem, cakey.pem).
|
Known issues
Due to security provider collisions between JCS and certain application
servers such as WebSphere, CA keys created by this tool are not
encrypted. This limitation can be easily fixed by replacing the "root"
CA certificate and key stored in the .globus/CA directory located in the user’s home, with custom certificate/key files from a third party CA such as VeriSign or Entrust.
|
Use the command line based tools
JCS provides command line tools similar to the openssl executable in the Globus Toolkit v3.
These tools provide similar functionality to the Web application including
CSR generation and signature plus certificate information.
Note: To enable certificate signature, a trusted or CA certificate
(cacert.pem) and private key (cackey.pem) must exist on $HOME/.globus/CA.
Create a certificate request
To create a certificate request, use the following command. On Windows and Linux, make sure the JCS_INSTALL_PATH environment variable is set to the installation directory.
jcs req –out /tmp/rq.pem –keyput /tmp/key.pem –pwd "mypwd"
|
Optional arguments are –dn "O=Grid, OU=Ogsa, OU=IT, CN=John Doe –bits 1024
Note: O, OU, CN are case sensitive.
To sign a certificate request:
To sign a certificate request, run the following command from your OS prompt (on Windows and Linux):
jcs ca –rq /tmp/req.pem –out /tmp/cert.pem
|
For this command to work, a trusted (CA) certificate must be installed in the user's
.globus/CA directory, thus $HOME/.globus/CA must exist and have two files:
cacert.pem and cakey.pem.
Optional arguments are: -cacert [path to CA cert] -cakey [path to the CA key] -capwd [CA pwd]
To get information on an X.509 certificate
To get information on an X.509 certificate, use the following command (on Windows and Linux):
jcs x509 –in /tmp/cert.pem –info
|
A sample output of this command would be:
Subject: C=US, O=Grid, OU=simpleCA, CN=John DoeHash: 945769
|
|
Known issues
During testing on application servers such as IBM WebSphere 4.x/5.x,
security provider collisions between BC and IBM JCE have been
discovered. The collision occurs when trying to encrypt private keys.
To bypass this issue, the default CA key installed by the Web
application is not encrypted, thus signing certificates requires no CA
password.
The CA cert and private key can be easily replaced with your own set of custom
certificates just by saving your CA cert and key in $HOME/.globus/CA as cacert.pem
and cakey.pem respectively (where $HOME represents the user’s home directory).
|
Create a binary distribution from source:
To build Java Certificate Services from source, you will need Apache ant configured in your system:
- Unzip the source distribution in your filesystem.
- Change to the source directory:
cd jCertServices
- Enter
ant all
- The binary distribution can be found within the source directory as
build/jCertServices-1.1.
The source was written using IBM WebSphere Studio 5.1. WebSphere developers can import the source into their workspace.
Download the source
The source code for Java Certificate Service is open source and available for download.
Feel free to look around and enhance it to suit your needs.
To build a binary Windows/Linux distribution, see the instructions above.
Conclusion
Enabling GSI security in your development grids can be a very
time-consuming activity, especially if you use a third-party
certificate authority such as Globus to sign your development
certificates. Productivity can be increased and the overall development
cycle can be reduced just by having your test grid up and running very
quickly. Java Certificate Services accomplishes this task by shielding
system administrators from the tedious task of issuing cert requests
for each machine, sending those requests to an outside entity for
signature and installing them.
Packages such as the Globus simple CA
provide this functionality, but Java Certificate Services has an upper
hand. It provides a Web-based tool that can be accessed via a Web
browser from any machine. This feature alone can save a great deal of
time. The full source code and binaries are provided in this article.
Feel free to look around Java Certificate Services and see if it fits
your grid development needs.
Resources
- Download the source code used in this article.
- Get more information on the Globus Toolkit at http://www.globus.org/.
- Visit the Globus Alliance at http://www.globus.org/
- Read up on grid security infrastructure at http://www-unix.globus.org/security/
- Read "A Java Commodity Grid Kit, Concurrency and Computation:
Practice and Experience," by Gregor von Laszewski, Ian Foster, Jarek Gawor, and Peter Lane, in the journal Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, vol. 13, no. 8-9, pp. 643-662, 2001, at http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/84503216/ABSTRACT.
- Learn more about the Java CoG Kit at http://www-unix.globus.org/cog/java and at http://www.cogkits.org.
- Get information on Cryptix (http://www.cryptix.org)
and the Legion of the Bouncy Castle (http://www.bouncycastle.org).
- Get Apache Tomcat at http://www.apache.org/. and Apache ant at http://ant.apache.org/.
- For information on IBM WebSphere Application Server, see http://www7b.software.ibm.com/wsdd/zones/was/.
Download
| Name | |  | | Size | |  | | Download method | |  | | gr-jsc/jcssource.zip | |  | | | |  | | FTP | |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
About the author
Vladimir
Silva was born in Quito, Ecuador. He received a Systems Analyst degree
from the Polytechnic Institute of the Army in 1994. In the same year,
he came to the United States as an exchange student pursuing an M.S.
career in Computer Science at Middle Tennessee State University. After
graduation, he joined the IBM "Web-Ahead" technology think tank. His
interests include Grid computing, Neural Nets, and artificial
intelligence. He also holds numerous IT certifications including OCP,
MCSD, and MCP. You can contact Vladimir at vsilva@us.ibm.com. |

| 
